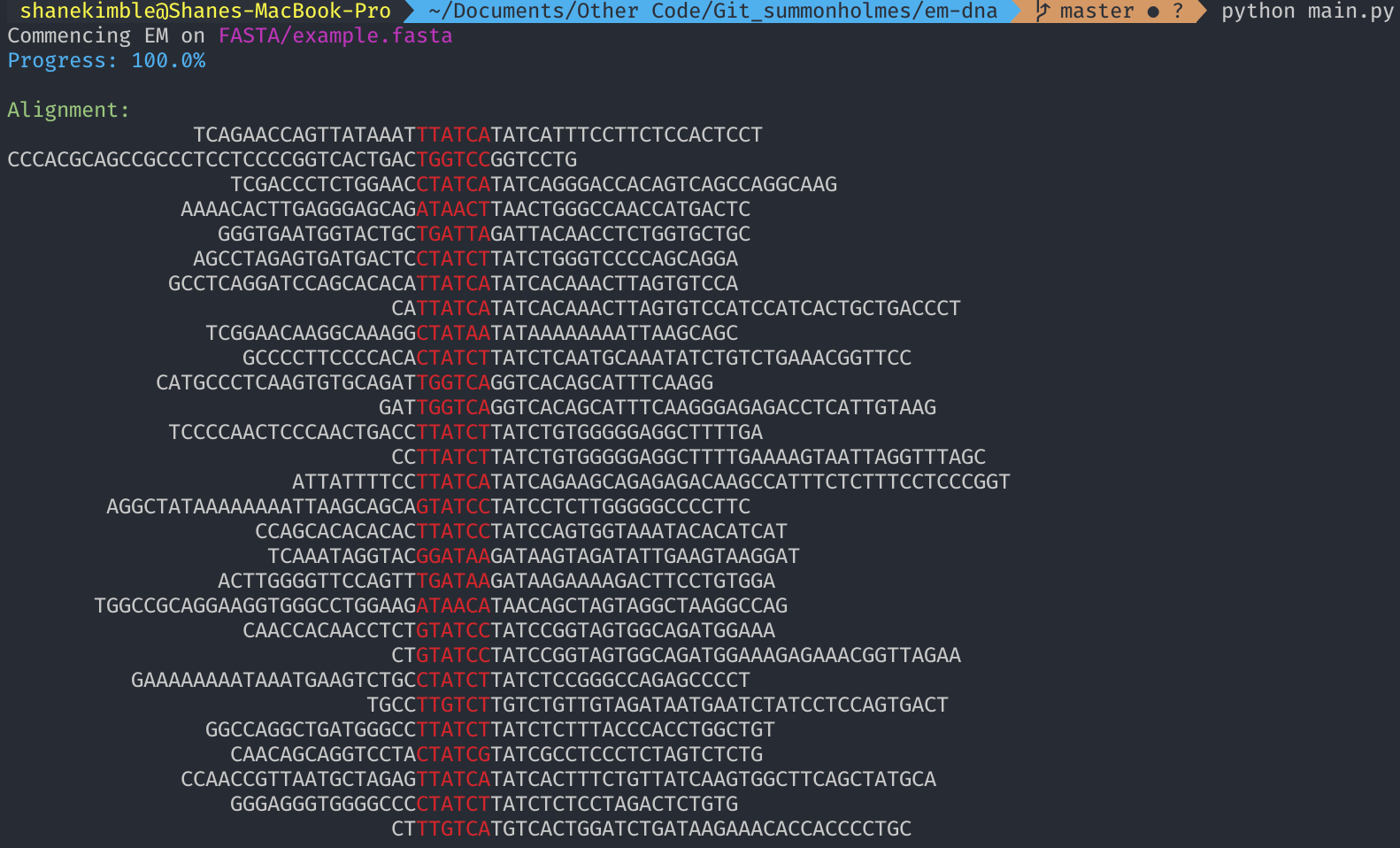
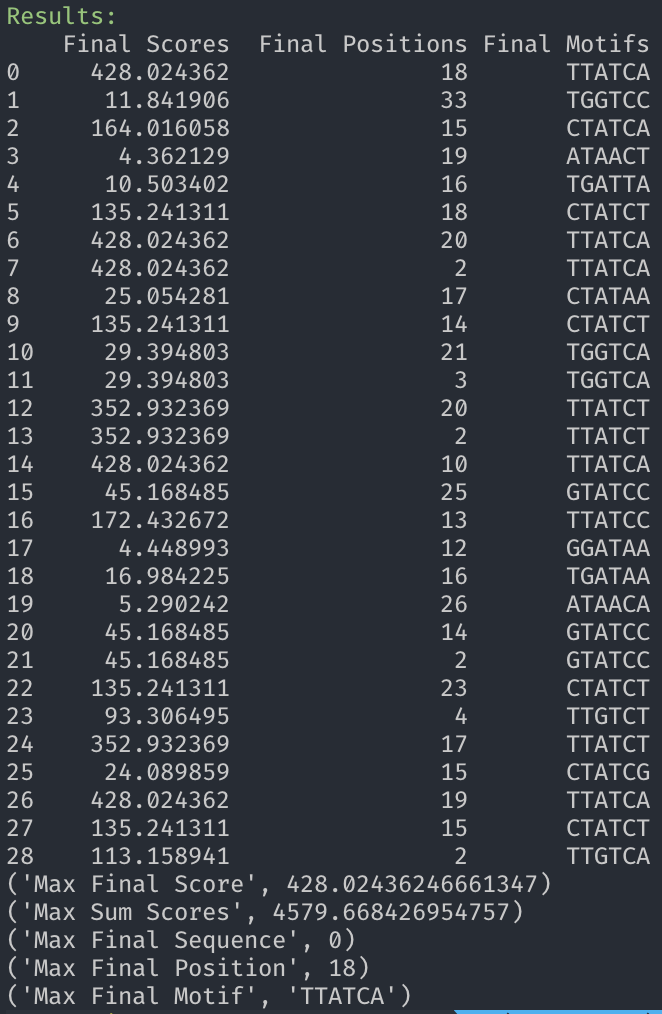
This is my implementation of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm performed on multiple DNA sequences. As a latent variable model, the EM algorithm is an example of unsupervised learning. The primary objectives of this program are to discover optimal alignment positions and motifs for multiple DNA sequences and to provide a clear and efficient EM implementation.
Optimal alignment positions and motifs are the latent variables requiring detection - meaning they are known to exist, are known to possess high importance, but are unable to be identified directly.
Since the starting positions of the DNA motifs are always randomized, no two runs are ever alike. However, when provided the same input more than once, the program results are almost always the same.
The Expectation (E) step composes the majority of source code. Total positional counts, frequencies, odds, then log-odds calculations compose the E step and derive the log-likelihood function. The Maximization Step scores on the log-likelihood function derived from the previous Expectation Step. Taking the score for every possible contiguous motif, for each sequence, the motif positions that generate the maximum scores on each sequence are identified, then become the input of the next E step. The E and M steps are then repeated X number of times. After enough iterations, convergence occurs to identify the optimal alignment positions and motifs.
An implementation in Julia is also available. The Julia implementation was constructed to test the claims regarding Julia's superior performance. Despite being as identical to the Python code blueprint as possible (minus the object-oriented structure), the Julia code runs far slower. Perhaps I can improve it once I learn more about Julia.
A brief description of the different files:
- class_EM_DNA: The object utilized to hold variables and methods for the entire process.
-
em_input: Loads all user data including the number of random alignments, the number of iterations, and the FASTA file. This function has an interactive mode, but this is commented out in favor of default parameters. The defaults include a motif width of 6, 50 total random alignments, and 50 iterations.
-
em_prep: Consolidates all consistent and reusable information. This includes all bases as a string, all base counts, all contiguous motifs, and cumulative sums.
-
em_process: The first iteration or 'for' loop over the number of random alignments. Previously, the entire program could be thought of as one gigantic, quintuple, nested 'for' loop. However, this approach has been reduced to a double 'for' loop via NumPy vectorization and indexing. This is the 'nucleus' of the program, which encompasses the entire EM process and iterates for the specified number of total random alignments.
-
em_count: Performs all counting operations regarding bases, motifs, and normalization. The only area where looping occurs is over the motif width when storing positional counts. The rest of this function aims to be as Pythonic and vectorized as possible.
-
em_matrix: Consists of the E step and generates the log odds matrix for the M step. NumPy matrices are preferred here for their vector capabilities.
-
em_run: Consists of the remaining 'for' loop mentioned above in em_process, and the M step. The entire process repeats to convergence, and the final results are printed in 'main.py'. Note that the function 'update_log_odds' is the entire Expectation Step and recycles all functions from em_count & em_matrix. The best results for the iteration are then recorded.
-
em_score: Scores are calculated using a NumPy character array for each motif and the log odds matrix. This is performed for each iteration in em_run.
-
em_finalize: Aligned DNA sequences, the scoring results for the aligned sequences, and the maximum statistics are displayed.
This program requires few dependences and should be trivial to set up. However, an in-depth understanding of the EM algorithm requires some knowledge of bioinformatics, data science, and machine learning.
- python3 (Python 3.6-3.11)
- numpy
- pandas
- termcolor
- colorama
$ virtualenv venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install numpy pandas termcolor colorama
$ python /path/to/main.py
python3.exe C:\path\to\main.py
This project is licensed under the GNU General Public License GPLv3.
Shane Kimble - summonholmes@protonmail.com - summonholmes