A stack is an ordered list where all insertions or deletions happen at one end, called the "top." A stack is also a limited-access data structure since you can only access elements from the top, which means stacks adhere to the "Last-In, First-Out" (LIFO) rule.
You can think of a stack like a you might a stack of ceramic plates. In order to access the third plate from the top, you need to safely remove the first two plates. These two plates limit access to the third, and since they were the most recent additions, they are the first that need to be removed.
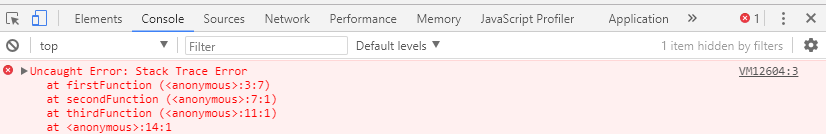
The call stack is one example of a stack. We've encountered it many times while debugging our JavaScript code, and it looks like this:
The call stack records the function calls that are made in a program. Each function creates a frame that is "pushed" to the top of the stack. This frame "pops" off once it returns its value.
- A stack of plates in a cupboard
- Reversing a string
- The undo tool in text editors
To reverse a string using a stack:
- Create an empty stack.
- One by one push all characters of string to stack.
- One by one pop all characters from stack and put them back to string.
Check for balanced parentheses in an expression:
-
Create an empty stack.
-
Traverse the expression string.
a) If the current character is a starting bracket ‘(‘ or ‘{‘ or ‘[‘ then push it to stack.
b) If the current character is a closing bracket ‘)’ or ‘}’ or ‘]’ then pop from stack. If the popped character matches the starting bracket then return true. Else, the parentheses are not balanced and the function returns false.
-
After complete traversal, if there are any starting brackets left in stack then the expression is “not balanced”.
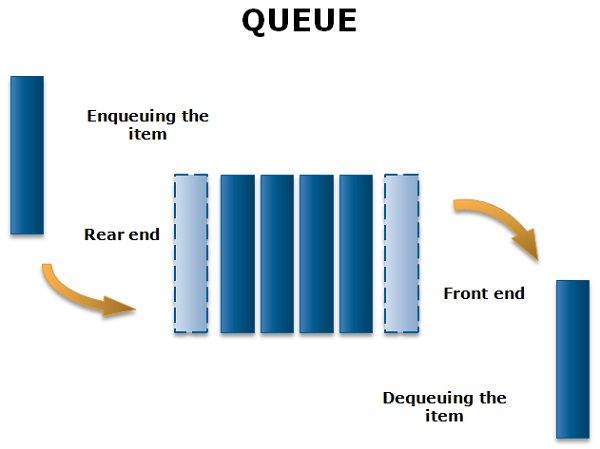
Queues are implemented using a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle, meaning that the items are removed from the list in exactly the same order in which they were added to it. For example, waiting in line at a fast food restaurant, whoever is in the front of the line will be helped first, and new customers are entered at the back of the line.
In the queue, only two operations are allowed, enqueue and dequeue. Enqueue means to insert an item into the back of the queue, dequeue means removing the front item.
- Data Buffers
- Asynchronous data transfer (file IO, pipes, sockets).
- Allotting requests on a shared resource (printer, processor).
- Traffic analysis.
- Determine the number of cashiers to have at a supermarket.
- A line of customers at the grocery store
- Call center phone systems
- Priority queue - values come out in order by priority, instead of FIFO. An element of highest priority always appears at the front of the queue. Operating systems use priority queues for load balancing on servers.
Queues can be helpful in any situation where data doesn't need to be accessed immediately and can be held in a buffer (the queue) or when you need to preserve the order of data, like when selling tickets. Some example interview questions regarding queues are:
- How to implement a queue using stacks?
- Which data structure is used for breadth-first search (BFS), traversing a tree?
Deque is a queue data structure that allows inserting items and deleting items at both ends. Four basic operations are performed on a deque:
- insertFront(): adds an item at the front of the deque
- insertLast(): adds an item at the rear of the deque
- deleteFront(): deletes an item from the front of the deque
- deleteLast(): deletes an item from the rear of the deque
Deques can be implemented using a doubly linked list or a circular array. Time complexity in both is O(1).
- HackerRank video on Data Structures: Stacks and Queues