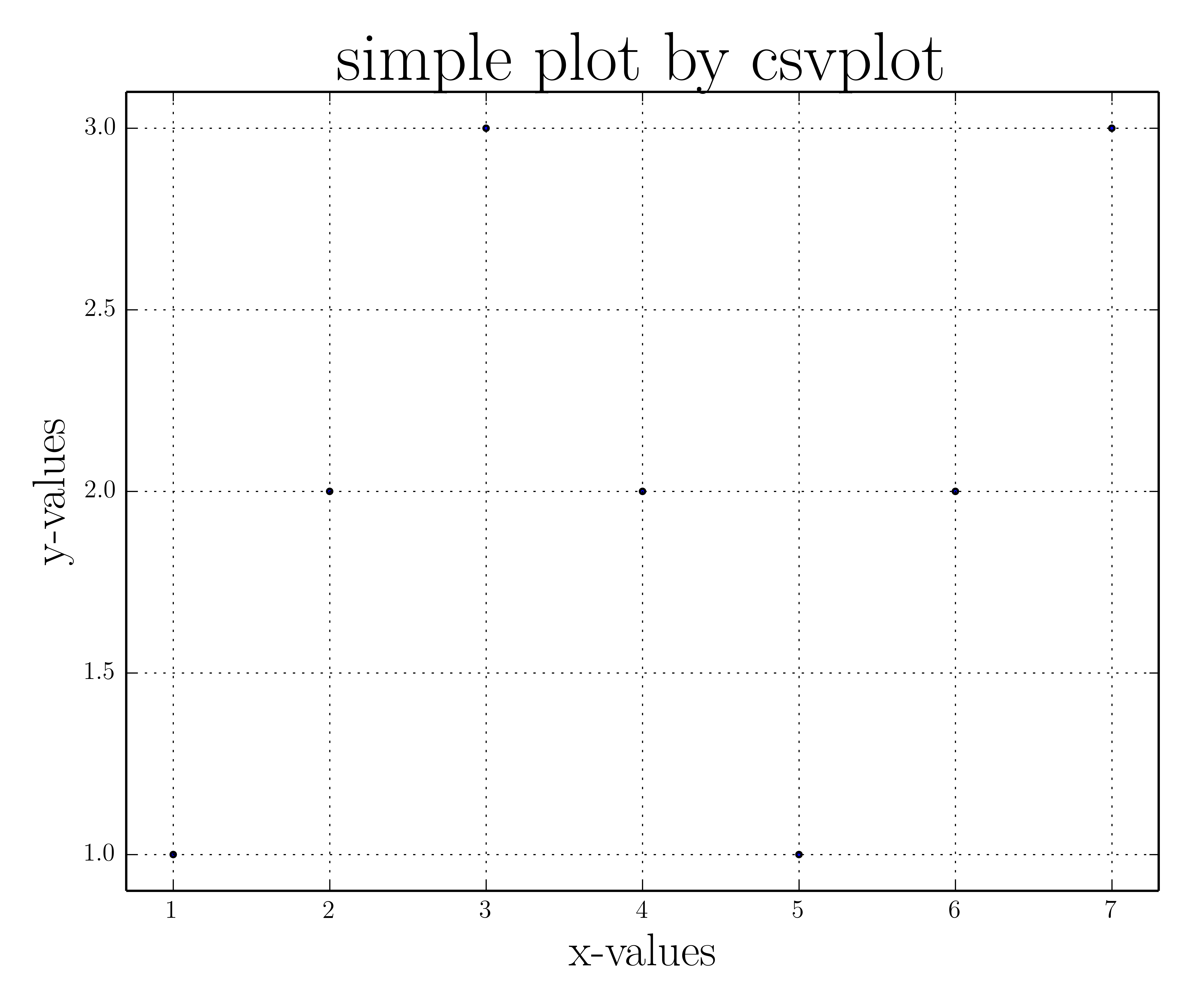
csvplot helps you to plot data in plaintext/csv format or from SQLite databases. Plots are customizable using csvplot features or by dropping back to Python/matplotlib functionality.
Basically, this means that csvplot is partially an application, partially a framework.
Plots can be re-generated when the data changes.
csvplot is written in Python and based on numpy/matplotlib.
Input is structured like this:
x,x**3
-3,-27
-2,-8
-1,-1
0,0
1,1
2,8
3,27
# works with python 2 and 3
python csvplot.py csvmode --nolatex --infile doc/data.csv --show
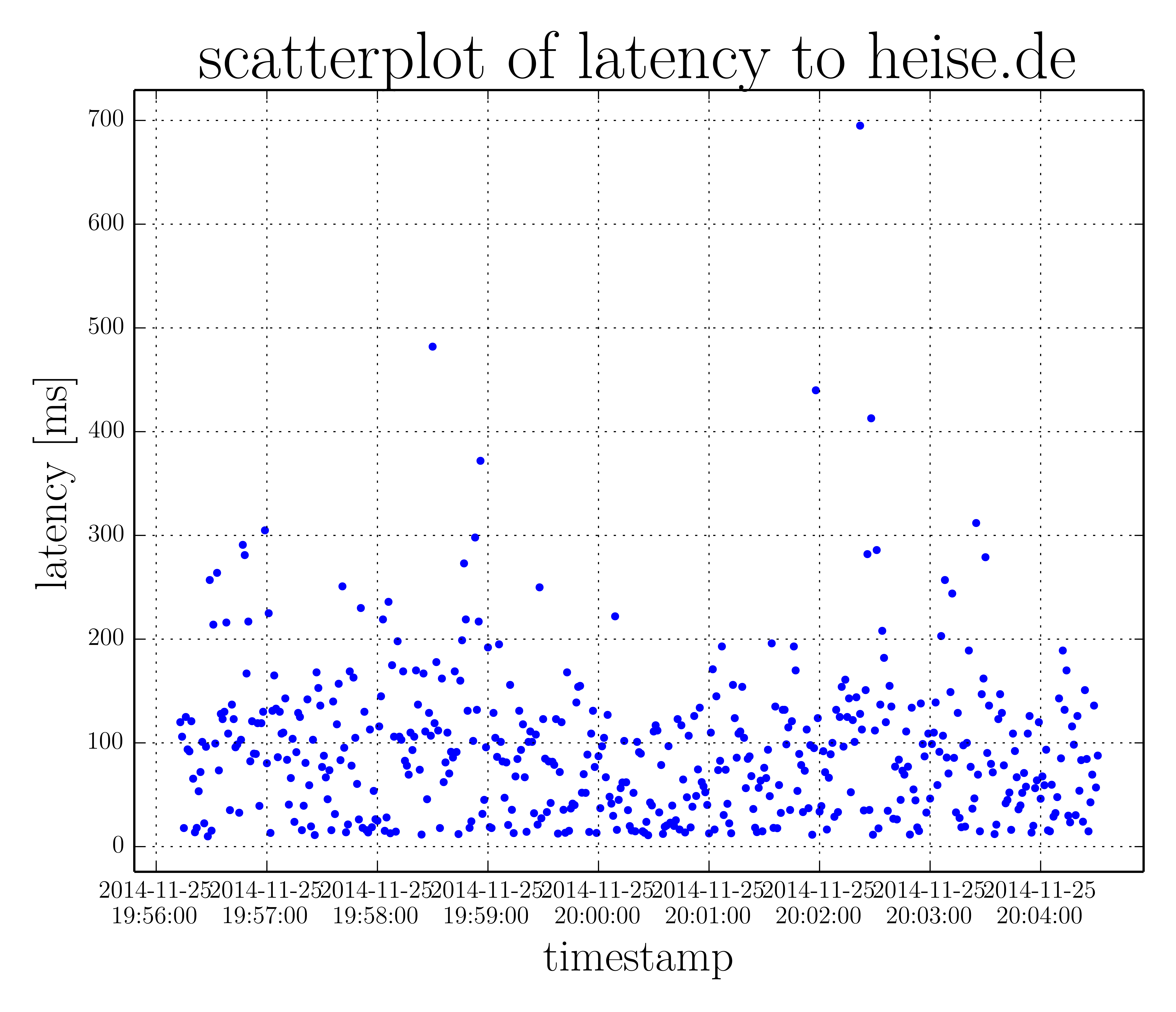
Input is structured like this:
timestamp num bytes from host ip seq ttl ping ms
2014-11-25@19:56:13 64 bytes from redirector.heise.de (193.99.144.80): icmp_seq=3395 ttl=245 time=120 ms
2014-11-25@19:56:14 64 bytes from redirector.heise.de (193.99.144.80): icmp_seq=3396 ttl=245 time=106 ms
2014-11-25@19:56:15 64 bytes from redirector.heise.de (193.99.144.80): icmp_seq=3397 ttl=245 time=17.9 ms
To obtain data like this yourself, run:
ping heise.de | while read pong; do echo "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d@%H:%M:%S') $pong"; done >> doc/ping.csv
You need to manually add the first header line and remove trailing statistics output added by ping (last few lines).
python csvplot.py csvmode --nolatex --infile doc/ping.csv --xy 1 9 --sep " " --xtransform date --ytransform ping --title "scatterplot of latency to heise.de" --xlabel "timestamp" --ylabel "latency [ms]" --show
regex2db.py allows to parse textfiles by regular expressions and write the data to a sqlite database.
csvplot.py supports a special sqlmode that allows reading data from a sqlite database.
The following example is basic as the power of SQL is not really used, but the principle should be clear.
The above ping example can be solved using the sqlite way as follows:
# create a database with suitable schema.
# any schema can be used
sqlite3 ping.sqlite <<EOF
CREATE TABLE data1 (timestamp TEXT, host TEXT, ip TEXT, ping REAL);
.exit
EOF
# fill the database from a log file.
python regex2db.py --dbfile ping.sqlite --tablename data1 --truncate \
--capture 1 date timestamp \
--capture 2 string host \
--capture 3 string ip \
--capture 4 float ping \
--regex '(\S{19}) 64 bytes from (\S+) \(([0-9.]+)\): icmp_seq=\d+ ttl=\d+ time=([0-9.]+) ms' \
doc/ping.csv
# run the csvplot in sqlmode.
python csvplot.py sqlmode --nolatex --dbfile ping.sqlite --sql 'select timestamp as x, ping as y from data1;' --xtransform date --title "scatterplot of latency to heise.de" --xlabel "timestamp" --ylabel "latency [ms]" --show
The SQL statement can have any complexity, but must select rows with (at least) the columns x and y containing the data to plot.
- Install the dependecies
sudo apt-get install python-matplotlib
Save csvplot.py anywhere and run it as described in the examples or the usage section.
$ python csvplot.py csvmode -h
usage: csvplot csvmode [-h] [--noheader] [--sep SEP] [--xy XY XY]
(--infile INFILE | --stdin) [--title TITLE]
[--xsize XSIZE] [--xtransform XTRANSFORM] [--xlog]
[--xlabel XLABEL] [--ysize YSIZE]
[--ytransform YTRANSFORM] [--ylog] [--ylabel YLABEL]
[--outfile OUTFILE] [--show] [--marker MARKER]
[--linestyle LINESTYLE] [--interact] [--nolatex]
[--dateformat DATEFORMAT] [--datelocator DATELOCATOR]
[-d] [-v]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--noheader if set, first line is data, not header (default:
False)
--sep SEP seperator used in csv file ala ','/' '/'\t' (default:
,)
--xy XY XY index of column for x and y data (default: None)
--infile INFILE csv file to open (default: None)
--stdin read from stdin (default: False)
--title TITLE graph title (default: simple plot by csvplot)
--xsize XSIZE size of graph (default: 8)
--xtransform XTRANSFORM
transformation for x values (float/date/ping)
(default: float)
--xlog use logarithmic x axis (default: False)
--xlabel XLABEL label for x axis (default: x-values)
--ysize YSIZE size of graph (default: 6)
--ytransform YTRANSFORM
see xtransform (default: float)
--ylog use logarithmic y axis (default: False)
--ylabel YLABEL label for y axis (default: y-values)
--outfile OUTFILE file to save plot to (default: None)
--show if set, opens plot in an interactive window (default:
False)
--marker MARKER matplotlib marker style ala ./x/o (default: .)
--linestyle LINESTYLE
matplotlib line style ala ''/-/. (default: )
--interact if set, drop to python shell before plotting (default:
False)
--nolatex if set, no latex is required to run (default: False)
--dateformat DATEFORMAT
date format used to parse dates (default:
%Y-%m-%d@%H:%M:%S)
--datelocator DATELOCATOR
where to put date markers ala auto/day/minute
(default: auto)
-d, --debug enable debug output (default: 30)
-v, --verbose enable verbose output (default: None)
$ python csvplot.py sqlmode -h
usage: csvplot sqlmode [-h] --dbfile DBFILE --sql SQL [--title TITLE]
[--xsize XSIZE] [--xtransform XTRANSFORM] [--xlog]
[--xlabel XLABEL] [--ysize YSIZE]
[--ytransform YTRANSFORM] [--ylog] [--ylabel YLABEL]
[--outfile OUTFILE] [--show] [--marker MARKER]
[--linestyle LINESTYLE] [--interact] [--nolatex]
[--dateformat DATEFORMAT] [--datelocator DATELOCATOR]
[-d] [-v]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dbfile DBFILE db file to open (default: None)
--sql SQL sql query that returns (at least) 'x' and 'y' data
(default: None)
--title TITLE graph title (default: simple plot by csvplot)
--xsize XSIZE size of graph (default: 8)
--xtransform XTRANSFORM
transformation for x values (float/date/ping)
(default: float)
--xlog use logarithmic x axis (default: False)
--xlabel XLABEL label for x axis (default: x-values)
--ysize YSIZE size of graph (default: 6)
--ytransform YTRANSFORM
see xtransform (default: float)
--ylog use logarithmic y axis (default: False)
--ylabel YLABEL label for y axis (default: y-values)
--outfile OUTFILE file to save plot to (default: None)
--show if set, opens plot in an interactive window (default:
False)
--marker MARKER matplotlib marker style ala ./x/o (default: .)
--linestyle LINESTYLE
matplotlib line style ala ''/-/. (default: )
--interact if set, drop to python shell before plotting (default:
False)
--nolatex if set, no latex is required to run (default: False)
--dateformat DATEFORMAT
date format used to parse dates (default:
%Y-%m-%d@%H:%M:%S)
--datelocator DATELOCATOR
where to put date markers ala auto/day/minute
(default: auto)
-d, --debug enable debug output (default: 30)
-v, --verbose enable verbose output (default: None)
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2014-2015 Michael Nagel and csvplot contributors
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.