követelmény:
-
- hét végig egy téma bejelentő
- zh/vizsga
- beadanó utolsó hét előttig
kapcsolódó anyagok:
- Build a Heroku Clone – Provision Infrastructure Programmatically - on YouTube, by freeCodeCamp.org: Code Your Own Heroku Clone with Python – Provision Infrastructure Programmatically Tutorial - on GitHub /herocool
Big Data
- massive volume of both structured, semi-structured and unstructured different type of data that has the potential to be mined for valuable information
- data is so large, complex, and rapidly growing therefore, it is overly difficult to process using traditional databases and software techniques
- Traditional sequential data processing algorithms are not sufficient to analyse this large volume of data. This phenomenon demands new strategies, techniques and tools
clouds?
- Cloud infrastructures are continuously emerging
- user-friendly way and on-demand solutions for complex problems
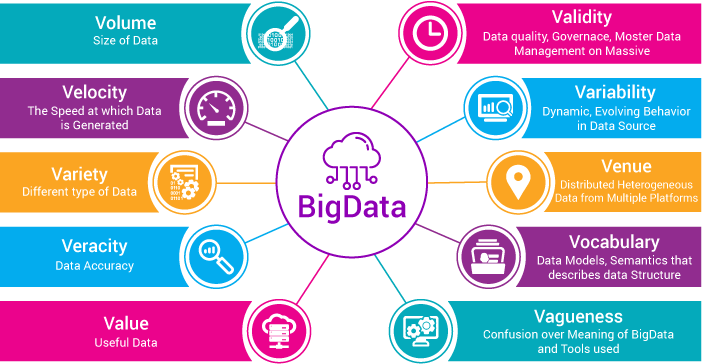
characteristics of Big Data - "The 10 V’s"
- volume: size of data
- velocity: the speed of data generation
- variety: different types of data
- veracity: data accuracy
- value: useful data
- validity: data quality
- variability: dynamic evolving in data structures
- venue: distriuted heterogenous data from multiple platforms
- vocabulary: data models
- vagueness: confusion over big data and tools used
- 2.5 trillion Gb/day
- 6 billlion people
- companies data
- 150 exabyte in healthvcare in 2011
- 4 billion+ hours watched on YouTube/month
- 400 million tweet/day
- 30 billion post/day on facebook
- 1 tb trade information /trading session
- ~100 sensor/car
- 18.9 billion network connection in 2016
positive spiral: more users generating more data leading to better algorithms creating better user experience resulting more users...
- poor data quality costs the US 3.1 trillion USD/year
- 27% of people is unsure of how much their data was inaccurate
Google Modular Computing Environment
- low-cost servers with directly attached disk storages
- Google hardware infrastructure consisted of hundreds of thousands of servers following modular approach
- note that no operating system or database platform available at the time could come close to operating across such a huge number of servers
- Google developed a hierarchical software stack with three major layers:
- Google File System (GFS): a distributed cluster file system that allows all of the disk capacities within the Google data center to be aggregated and accessed as one massive, distributed, redundant file system.
- MapReduce: a distributed processing framework for parallelizing algorithms across large numbers of potentially unreliable servers and being capable of dealing with massive datasets.
- BigTable: a nonrelational database system that uses the GFS for storage.
provides general-purpose parallelization of data-intensive processing
- mapping phase: data is split into smaller chunks that can be processed easier by separate threads—potentially running on separate machines
- a reduce phase: it combines the output into the final result
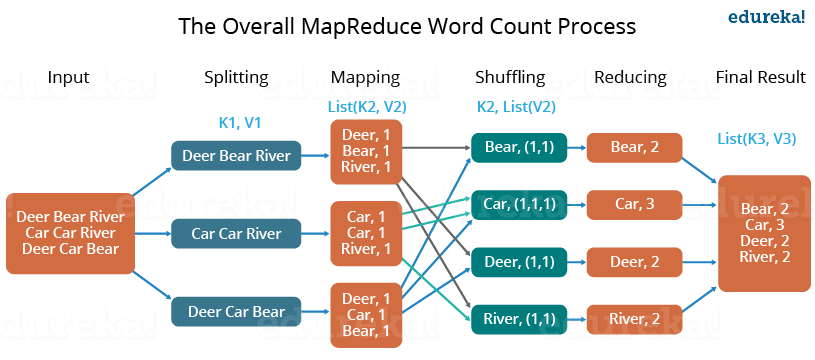
ex: word-count program
- the program counts the occurrences of pet types in the given input files – by breaking the data into equal chunks in the map phase – then the data is shuffled into groups of pet types – finally, the reduce phase sums the occurrences that is fed into the output
multiple MapReduce phases might be also chained each after another to achieve more complex results
- multiple input files to be merged in a given way
- some complex iterative processing to perform a statistical or machine learning analysis
more complex multi-stage MapReduce pipeline:
- a file containing information about visits to various product webpages is joined with
- a file containing product details — to obtain the product category — and then joined again to
- a file containing customer details, so as to determine the customer’s country
- this joined data is then aggregated to provide a report of product categories, customer geographies, and page visits
Equivalent SQL query:
SELECT prod_category, Cust_country, SUM(visits) FROM products JOIN product_page_visits USING (prod_id) JOIN customers USING (cust_id) GROUP BY prod_category, Cust_country
Hadoop: Open-Source Google Stack
develops open-source software for reliable, scalable, distributed computing
- An economical scalable storage model. As data volumes increase, so does the cost of storing that data online. Because Hadoop can run on commodity hardware that in turn utilizes commodity disks, the price point per terabyte is lower than that of almost any other technology
- Massive scalable IO capability. Because Hadoop uses a large number of commodity devices, the aggregate IO and network capacity is higher than that provided by dedicated storage arrays in which smaller numbers of larger disks are provided by even smaller numbers of processors
- adding new servers to Hadoop adds storage, IO, CPU, and network capacity all at once, whereas adding disks to a storage array might simply exacerbate a network or CPU bottleneck within the array
- Reliability Data in Hadoop is stored redundantly in multiple servers using HDFS (Hadoop File System) and can be distributed across multiple computer racks. Failure of a server does not result in a loss of data; in fact, a Hadoop job will continue even if a server fails — the processing simply switches to another server
- A scalable processing model: MapReduce represents a widely applicable and scalable distributed processing model. While MapReduce is not the most efficient implementation for all algorithms, it is capable of brute-forcing acceptable performance for almost all.
- Schema on read: Data can be loaded into Hadoop without having to be converted to a highly structured normalized format. This makes it easy for Hadoop to quickly ingest data from various forms. The imposition of structure can be delayed until the data is accessed; this is sometimes referred to as schema on read (in opposite to the schema on write mode of relational data warehouses)
Survey questions
- Why is not the size of data the only factor that matters when we are speaking about Big Data?
- What was the role of Google in the evolution of Big Data platforms?
Google Modular Computing environment => GFS
What are the 5 steps of MapReduce paradigm?
input, split, mapping, schuffle, reduce, final
Why Hadoop is a so scalable platform?
"This is in essence how Hadoop behaves. Imagine each rack or computer in the Hadoop cluster being a floor of the Hadoop hotel and rather than the data moving between floors we take the calculation instructions (or cook) to the machine where the data is living." ~ intricity
Követelmények:
- zh: MS Teams szóbeli / írásbeli
- féléves feladat +/- 1
-
- héten zh pótlás vagy féléves feladat pótlás
-
- vizsga: megajánlott jegy a félévi teljesítmény alapján (4/5) vagy vizsga
- using Hadoop HDFS as its file system, HBase is able to create tables of truly massive size—way beyond the possible size for a system like MySQL, or even for Oracle
- In addition, the fault tolerance of HDFS provides automatic redundancy for HBase tables
- HBase tables vary significantly from relational tables:
- in each cell — a column value for a particular row— there will usually be multiple versions of a data value. Each version of data within a cell is identified by a timestamp. This provides HBase tables with a sort of temporal “third dimension.”
- HBase columns are more similar to the key values
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lSrNUyMR_Ek
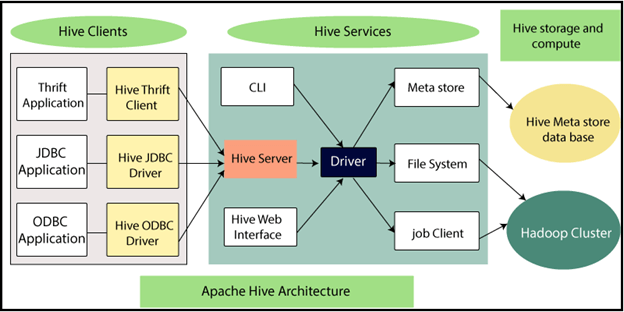
- Hive provides a catalog for the Hadoop system, as well as a SQL processing layer
- The Hive metadata service contains information about the structure of registered files in the HDFS file system
- Hive client or server (depending on the Hive configuration) accepts SQL-like commands: HQL
- Performance:
- The predominant Hadoop vendor Cloudera has created an alternative proprietary SQL on the Hadoop framework called Impala
- others (including another major Hadoop vendor Hortonworks) have attempted to improve Hive’s performance through incremental changes and better integration with post- MapReduce frameworks such as YARN and Tez
| Hive | Apache Hbase |
|---|---|
| query language | data storage particulary for unstructured data |
| Apache Hive is a minly used for batch processing ie: OLAP | HBase is extensively used for transactional processing wherein the response time of the query is not highly interactive ie: Online transaction processing |
| operations are transformed into mapreduce | operations are run in real-time on the DB |
| analytical queries | real-time querying |
more: hevodata.com
- Memcached is an open-source utility that provides a distributed object cache
- Object-oriented languages could cache an object-oriented representation of database information across many servers
- reading from these servers rather than the database, the load on the database could be reduced
- Web developers took advantage of MySQL replication:
- read: from any replica
- write to master
a logical database to be partitioned across multiple physical servers
- the largest tables are partitioned across multiple database servers
- Each partition is referred to as a
shard- This partitioning is based on a Key Value, such as a userID
- When operating on a particular record, the application must determine which shard will contain the data and then send the SQL to the appropriate server
- Application complexity. It is up to the application code to route SQL requests to the correct shard
- statically sharded database, this would be hard enough
- massive websites are adding shards as they grow, which means that a dynamic routing layer must be implemented
- Crippled SQL it is not possible to issue a SQL statement that operates across shards
- Loss of transactional integrity ACID transactions against multiple shards are not possible — or at least not practical: Two Phase Commit
- Operational complexity Adding new shards requires a complex rebalancing of data. Changing the database schema also requires a rolling operation across all the shards, resulting in transitory inconsistencies in the schema
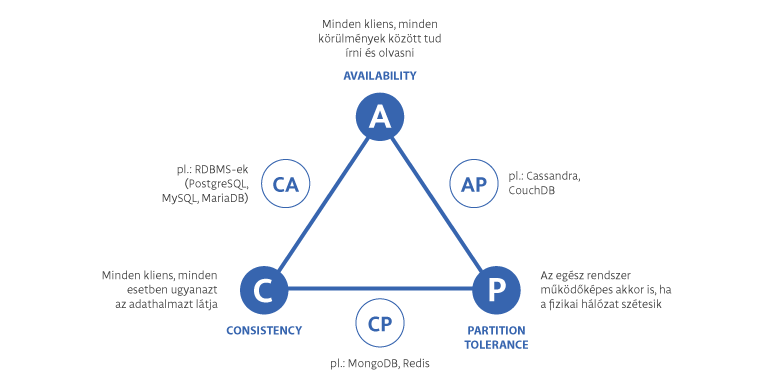
in a distributed database system, you can have at most only two of:
- Consistency: every user of the database has an identical view of the data at any given instant.
- Availability: in the event of a node failure, the database remains operational
- Partition tolerance: the database can maintain operations in the event of the network’s failing between two segments of the distributed system
if you want your system to be undisturbed by network partitions, you must sacrifice strict consistency between partitions.
for social networks and certain e-commerce operations, this worldwide synchronous consistency is unnecessary
Tunable Consistency Amazon Dynamo allows the application to choose the level of consistency applied to specific operations.:
- N is the number of copies of each data item that the database will maintain.
- W is the number of copies of the data item that must be written before the write can complete.
- R is the number of copies that the application will access when reading the data item.
When W = N, Dynamo will always write every copy before returning control to the application. This is ACID
- N > W > 1 i.e. more than one write must complete, but not all nodes need to be updated immediately
- W + R > N this ensures that the latest value will always be included in a read operation, even if it is mixed in with “older” values.
Survey questions
- What is the main mechanism behind HIVE?
- SQL layer over Hadoop, using HQL commands
- client/server HQL commands => run in Hadoop => run on HDFS files => back to Hive
- Explain at least three of the drawbacks of sharding!
- the SQL querryes should be driven to shards can't operate across shards!
- in case of fragmentated databases can't run querryes on shards
- inserting new shard is wery difficult
- ACID transactions against multiple shards are not possible
- How would you set the NWR parameters in order to ensure that the value(s) of last write operation can be accessed during the upcoming read operations?
- W + R > N
vm: https://ubuntu.com/download/server
- client:
docker builddocker pulldocker run - docker host: futtatja a daemon által létrehozott rendszerű konténert
- registry: daemonok beállítják az imaget
docker hub imagek: https://hub.docker.com/search?image_filter=official&type=image
ha rootként privilegizált módban futtatjuk a usert akkor a kinti rendszerhez is hozzáfér => read only fájlhozzáférés megoldás lehet
10.0.2.15/24 user Almafa123
10.0.2.15/24 10.0.2.0/24 10.0.2.2
The structure of a JSON object is as follows:
- The data are in name/value pairs
- Data objects are separated by commas
- Curly braces {} hold objects
- Square brackets [] hold arrays Each data element is enclosed with quotes "" if it is a character, or without quotes if it is a numeric value
- Vertical scaling refers to increasing the processing power of a single server or cluster.
- Horizontal scaling, also known as scale-out, refers to bringing on additional nodes to share the load.
- SQL lacks the syntax to easily perform graph traversal, especially traversals where the depth is unknown or unbounded.
- Performance degrades quickly as we traverse the graph. Each level of traversal adds significantly to query response time.
- While RDF is an important graph technology, the Property Graph model provides a richer model for representing complex data by associating both nodes and relationships with attributes.
- Neo4j implements a declarative graph query language Cypher. Cypher allows graphs to be queried using simple syntax somewhat comparable to SQL or SPARQL, but particularly ptimized for graph traversals
Beadandóról
- dokumentáció
- prezentáció
Minden egyes változatás után új réteg a képfájlon
Kötetek hosszú távú tárolásra jók
Docker volume
Portman Docker helyett mint freeware megoldás.
több erőforrás csoportba szervezve is képes kiadni a nekünk szükséges erőforrást
erre jó a Kubernetees vagy Docker swarm - > clusterek hozhatóak létre
. Swarmban a titkosítás könnyebb
Nginx szolgáltatás -> minden állomáson kiosztunk egy replikát; belső kommunikáció tlsen zajlik.
Managerek egymás közt leadert választanak, a leaderek leaderét a leaderek választják.
Node balancerrel is rendelkeznek, node vagy cluster portot is megadhatunk. Let's encrypt szolgáltatása is használható.
- oszlop - idősoros adat
- gráf alapú - kapcsolatok
- dokumentum tároló - mongo db
CAP tétel
- rendelkezésre állás
- konzisztencia
- partíció tolerálás
- skálázhatóság
- sok elérhető típusú adatbázis
- változatos adatstruktúrák
- objektum alapú adattárolás
docker run --name some-cassandra --network some-network -d cassandra:3.11
docker exec -it some-cassandra bash
cqlsh -u cassandrahttps://learn.netdata.cloud/docs
wget -O /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh && sh /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh
alert manager: https://medium.com/devops-dudes/prometheus-alerting-with-alertmanager-e1bbba8e6a8e
- prometheus
- prometheus nem tárolásra lett kitalálva
- hosszútávú tárolási megoldások:
docker compose up letölti az aktuális prometheus képfájlt
nincs processor specifikus információ szolgáltatás
style guide -> more readable, docs can be generated from code, easier to maintain, easier to expand
version numbering: MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
- MAJOR: inkompatibilis változások
- MINOR: funkcionalitásában változik, de visszafele kompatibilis
- PATCH: visszafelé kompatibilis verzió, bugok javítás
egyéb alverziósámok hozzzáadhatóak a fejlesztés követése érdekében
az első publikus elérhető verzió legyen 0.1.0
- menetközben buildelni
- unit testeket végez menet küzben
- magát a keretrendszert felépíteni
- self hosted
- integrációs vagy rendszerfelépíési testek
- release naplót tud készíteni
- hírt tud automatizálni
- lehet self hosted
- konténert tud létrehozni automatikusan
The memory efficiency of column oriented and in-memory databases are really high. However, it has effect on (possible slow) loading data into to database.
- In-memory databases may provide efficient database solutions but ensure the persistency of data requires special mechanisms.
- The most widespread “swiss-knife” for Big Data, the SPARK framework overcomes the limitations of Hadoop by applying (among others) in-memory approach.
- The various big data platforms are available under different brands but with similar services.
- documents row in relation databases - one or more key-value pairs
- collections table in relational db - a set of documents
Using Sharding mongodb supports horizontal scaling. Horizontal Scaling involves dividing the system dataset and load over multiple servers, adding additional servers to increase capacity as required.
there is no syntaxes in sql for graphs => performance of SQL queries degrades as we iterate on graph levels.
- Neo4j: graph db
- MongoDB: document db
- skálázhatóság
- sok elérhető típusú adatbázis
- változatos adatstruktúrák
- objektum alapú adattárolás
docker run --name some-cassandra --network some-network -d cassandra:3.11
docker exec -it some-cassandra bash
cqlsh -u cassandrahttps://learn.netdata.cloud/docs
wget -O /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh && sh /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh
alert manager: https://medium.com/devops-dudes/prometheus-alerting-with-alertmanager-e1bbba8e6a8e
column based DBs use delta store, hich optimize the writing in db. The delta store is ram not on disks. Row orinentated inserts are stored in delta store, using parallel programming. The datasest are stored asynchonously.
- usefull:
- in a columnar architecture, queries that seek to aggregate the values of specific columns are optimized
- compression
- useless:
- too many writing
- reading just a row
Explain the details of SPARK architecture that allow the users to overcome the limitations of Hadoop?
- speeed - based on ram
- fault-tolerant processing
- there is no iteration
- usage of DAG (graphs)
- better than Map Reduce
- better for machine learning
- resilient distributed datasets
- collections of objects that can be partitioned across multiple nodes; handled automatically by the Spark framework
- The RDDs are constant immutables.
- the actions on RDDs give as result also RDD-s
- the readed values in Spark allways became RDDs
- The Spark API defines high-level methods that perform operations on RDDs.
- RDD contain key-value pairs, and Spark provides specific data manipulation operations such as aggregation and joins that work only on key-value oriented RDDs
- prometheus
- prometheus nem tárolásra lett kitalálva
- hosszútávú tárolási megoldások:
docker compose up letölti az aktuális prometheus képfájlt
nincs processor specifikus információ szolgáltatás
Open-source management platform for provisioning, managing, monitoring, and securing Apache Hadoop clusters. Using it provides secure configuration and desing of Hortonworks Data Platform.
- Simplified Installation, Configuration and Management
- Centralized Security Setup
- Full Visibility into Cluster Health
- visualization of critical warnings
- better security with Kerberos
- automatized clusters with Ambari Blueprints
- API for clusters
- create rerusable blueprints
- better reusability, easier cluster installation
- don't have to use web ui
- pick a Blueprint: Cloudbreak uses Ambari Blueprints to have declarative Hadoop cluster definition. Blueprints can be designed for specialized applications and workloads (such as Data Science or IoT Apps)
- Choose a Cloud: Cloudbreak is configured to work with cloud infrastructure resources (such as servers, network setup and security options)
- Launch Cluster: In this step, Cloudbreak obtains the chosen cloud infrastructure platform, installs Apache Ambari, and applies the desired Blueprint
style guide -> more readable, docs can be generated from code, easier to maintain, easier to expand
version numbering: MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
- MAJOR: inkompatibilis változások
- MINOR: funkcionalitásában változik, de visszafele kompatibilis
- PATCH: visszafelé kompatibilis verzió, bugok javítás
egyéb alverziósámok hozzzáadhatóak a fejlesztés követése érdekében
az első publikus elérhető verzió legyen 0.1.0
- menetközben buildelni
- unit testeket végez menet küzben
- magát a keretrendszert felépíteni
- self hosted
- integrációs vagy rendszerfelépíési testek
- release naplót tud készíteni
- hírt tud automatizálni
- lehet self hosted
- konténert tud létrehozni automatikusan
read the docs
- Cloud orchestration tool: distributed virtual infrastructure and configuration in one or more cloud based systems
- lightweight easily deployable
- hybrid cloud orchestration
- Open source
- single / multi environments
posible actions:
- Start a new node
- Delete a node
- Restart node
continuous monitoring of the infrastructure
- Resource definition: Defines the target resource, Cloud interface endpoints, Where the actual VM instance is, necessary to define
- Config management: Calibrates Server endpoints, optinonal
- Health check: How the servers running, how the node can be monitored ie: ping, url check, port check, database check , optinal
- Contextualisation: How the instanced VM contextualised, optinal
- rometheus monitoring tool for moniitoring clusters
- alert at specific usage
- occopus executors
- add or delet a slave from system
Occopus is cheaper, but HDInsight has more feature, constantly developed, and maintained.
- nomad : claster manager, mint a kubernetes
- ansible