链表相关的核心点
- null/nil 异常处理
- dummy node 哑巴节点
- 快慢指针
- 插入一个节点到排序链表
- 从一个链表中移除一个节点
- 翻转链表
- 合并两个链表
- 找到链表的中间节点
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None:
return head
current = head
while current.next is not None:
if current.next.val == current.val:
current.next = current.next.next
else:
current = current.next
return head给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现的数字。
- 思路:链表头结点可能被删除,所以用 dummy node 辅助删除
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None:
return head
dummy = ListNode(next=head)
current, peek = dummy, head
find_dup = False
while peek.next is not None:
if peek.next.val == peek.val:
find_dup = True
peek.next = peek.next.next
else:
if find_dup:
find_dup = False
current.next = current.next.next
else:
current = current.next
peek = peek.next
if find_dup:
current.next = current.next.next
return dummy.next注意点 • A->B->C 删除 B,A.next = C • 删除用一个 Dummy Node 节点辅助(允许头节点可变) • 访问 X.next 、X.value 一定要保证 X != nil
反转一个单链表。
- 思路:将当前结点放置到头结点
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None:
return head
tail = head
while tail.next is not None:
# put tail.next to head
tmp = tail.next
tail.next = tail.next.next
tmp.next = head
head = tmp
return head- Recursive method is tricky
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
rev_next = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return rev_next反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
- 思路:先找到 m 处, 再反转 n - m 次即可
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
if head is None:
return head
n -= m # number of times of reverse
curr = dummy = ListNode(next=head)
while m > 1: # find node at m - 1
curr = curr.next
m -= 1
start = curr.next
while n > 0: # reverse n - m times
tmp = start.next
start.next = tmp.next
tmp.next = curr.next
curr.next = tmp
n -= 1
return dummy.next将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
- 思路:通过 dummy node 链表,连接各个元素
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
tail = dummy = ListNode()
while l1 is not None and l2 is not None:
if l1.val > l2.val:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
else:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
tail = tail.next
if l1 is None:
tail.next = l2
else:
tail.next = l1
return dummy.next给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
- 思路:将大于 x 的节点,放到另外一个链表,最后连接这两个链表
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: ListNode, x: int) -> ListNode:
p = l = ListNode()
q = s = ListNode(next=head)
while q.next is not None:
if q.next.val < x:
q = q.next
else:
p.next = q.next
q.next = q.next.next
p = p.next
p.next = None
q.next = l.next
return s.next哑巴节点使用场景
当头节点不确定的时候,使用哑巴节点
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
- 思路:归并排序,slow-fast找中点
class Solution:
def _merge(self, l1, l2):
tail = l_merge = ListNode()
while l1 is not None and l2 is not None:
if l1.val > l2.val:
tail.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
else:
tail.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
tail = tail.next
if l1 is not None:
tail.next = l1
else:
tail.next = l2
return l_merge.next
def _findmid(self, head):
slow, fast = head, head.next
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
return slow
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
mid = self._findmid(head)
tail = mid.next
mid.next = None # break from middle
return self._merge(self.sortList(head), self.sortList(tail))注意点
- 快慢指针 判断 fast 及 fast.Next 是否为 nil 值
- 递归 mergeSort 需要断开中间节点
- 递归返回条件为 head 为 nil 或者 head.Next 为 nil
给定一个单链表 L:L→L→…→L__n→L 将其重新排列后变为: L→L__n→L→L__n→L→L__n→…
- 思路:找到中点断开,翻转后面部分,然后合并前后两个链表
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
prev, curr = None, head
while curr is not None:
curr.next, prev, curr = prev, curr, curr.next
return prev
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
if head is None or head.next is None or head.next.next is None:
return
slow, fast = head, head.next
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
h, m = head, slow.next
slow.next = None
m = self.reverseList(m)
while h is not None and m is not None:
p = m.next
m.next = h.next
h.next = m
h = h.next.next
m = p
return给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
- 思路1:Hash Table 记录所有结点判断重复,空间复杂度 O(n) 非最优,时间复杂度 O(n) 但必然需要 n 次循环
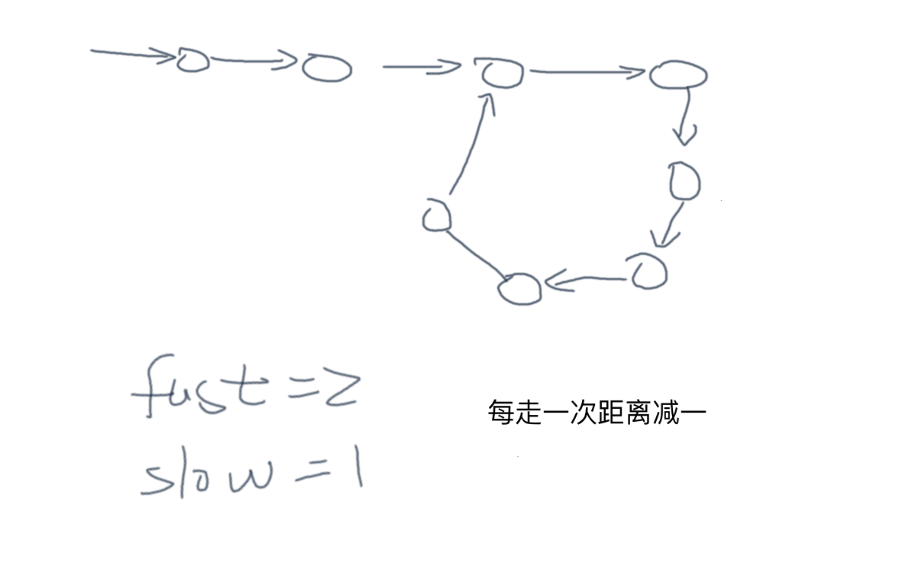
- 思路2:快慢指针,快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减 1,空间复杂度 O(1) 最优,时间复杂度 O(n) 但循环次数小于等于 n
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
slow = fast = head
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast == slow:
return True
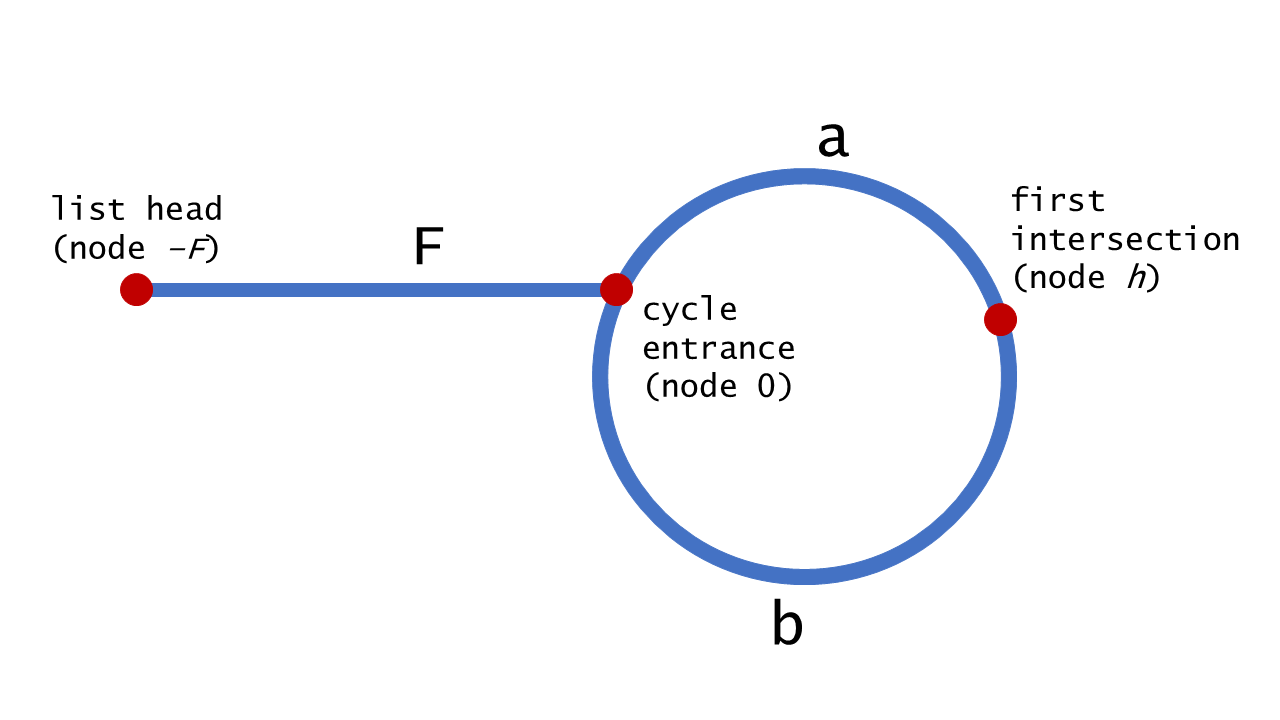
return False给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回
null。
- 思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点。
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
slow = fast = head
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
slow = head
while fast != slow:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return slow
return None坑点
- 指针比较时直接比较对象,不要用值比较,链表中有可能存在重复值情况
- 第一次相交后,快指针需要从下一个节点开始和头指针一起匀速移动
注意,此题中使用 slow = fast = head 是为了保证最后找环起始点时移动步数相同,但是作为找中点使用时一般用 fast=head.Next 较多,因为这样可以知道中点的上一个节点,可以用来删除等操作。
- fast 如果初始化为 head.Next 则中点在 slow.Next
- fast 初始化为 head,则中点在 slow
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
- 思路:O(1) 空间复杂度的解法需要破坏原链表(找中点 -> 反转后半个list -> 判断回文),在实际应用中往往还需要复原(后半个list再反转一次后拼接),操作比较复杂,这里给出更工程化的做法
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
s = []
slow = fast = head
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
s.append(slow.val)
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast is not None:
slow = slow.next
while len(s) > 0:
if slow.val != s.pop():
return False
slow = slow.next
return True给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。 要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
- 思路1:hash table 存储 random 指针的连接关系
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if head is None:
return None
parent = collections.defaultdict(list)
out = Node(0)
o, n = head, out
while o is not None:
n.next = Node(o.val)
n = n.next
if o.random is not None:
parent[o.random].append(n)
o = o.next
o, n = head, out.next
while o is not None:
if o in parent:
for p in parent[o]:
p.random = n
o = o.next
n = n.next
return out.next- 思路2:复制结点跟在原结点后面,间接维护连接关系,优化空间复杂度,建立好新 list 的 random 链接后分离
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if head is None:
return None
p = head
while p is not None:
p.next = Node(p.val, p.next)
p = p.next.next
p = head
while p is not None:
if p.random is not None:
p.next.random = p.random.next
p = p.next.next
new = head.next
o, n = head, new
while n.next is not None:
o.next = n.next
n.next = n.next.next
o = o.next
n = n.next
o.next = None
return new链表必须要掌握的一些点,通过下面练习题,基本大部分的链表类的题目都是手到擒来~
- null/nil 异常处理
- dummy node 哑巴节点
- 快慢指针
- 插入一个节点到排序链表
- 从一个链表中移除一个节点
- 翻转链表
- 合并两个链表
- 找到链表的中间节点