- Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Virtual Network Computing (VNC)
- Windows Remote Management (or PowerShell Remoting) (WinRM)
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
RDP listens by default on logical port 3389. By default, remote access is not allowed on Windows operating systems.
If we are connecting to a Windows target from a Windows host, we can use the built-in RDP client application called Remote Desktop Connection (mstsc.exe).
Remote Desktop Connection also allows us to save connection profiles. As pentesters, we can benefit from looking for these saved Remote Desktop Files (.rdp) while on an engagement.
FAT32 (File Allocation Table), where 32 refers to the fact that FAT32 uses 32 bits of data for identifying data clusters on a storage device.
-
Pros of FAT32:
- Device compatibility - it can be used on computers, digital cameras, gaming consoles, smartphones, tablets, and more.
- Operating system cross-compatibility - It works on all Windows operating systems starting from Windows 95 and is also supported by MacOS and Linux.
-
Cons of FAT32:
- Can only be used with files that are less than 4GB.
- No built-in data protection or file compression features.
- Must use third-party tools for file encryption.
NTFS (New Technology File System) is the default Windows file system since Windows NT 3.1. In addition to making up for the shortcomings of FAT32, NTFS also has better support for metadata and better performance due to improved data structuring.
-
Pros of NTFS:
- NTFS is reliable and can restore the consistency of the file system in the event of a system failure or power loss.
- Provides security by allowing us to set granular permissions on both files and folders.
- Supports very large-sized partitions.
- Has journaling built-in, meaning that file modifications (addition, modification, deletion) are logged.
-
Cons of NTFS:
- Most mobile devices do not support NTFS natively.
- Older media devices such as TVs and digital cameras do not offer support for NTFS storage devices.
The Server Message Block protocol (SMB) is used in Windows to connect shared resources like files and printers.
Share permissions and NTFS basic permissions are not the same but often apply to the same shared resource.
- Full control
- Change
- Read
- Full control
- Modify
- List Folder Contents
- Read & Execute
- Write
- Read
- Full control
- Traverse folder / execute file
- List folder/read data
- Read attributes
- Read extended attributes
- Create files/write data
- Create folders/append data
- Write attributes
- Write extended attributes
- Delete sub-folders and files
- Delete
- Read permission
- Change permission
- Take ownership
Computer Management is a tool we can use to identify and monitor shared resources on a Windows system.
Event Viewer is another good place to investigate actions completed on Windows.
Windows services are managed via the Service Control Manager system, accessible via the services.msc MMC add-in.
It is also possible to query and manage services via the command line using sc.exe using PowerShell cmdlets such as Get-Service.
Get-Service | ? {$_.Status -eq "Running"} | select -First 2 |fl
If we update any file or resource in use by a critical system services, we must restart the system.
lsass.exe is the process that is responsible for enforcing the security policy on Windows systems. When a user attempts to log on to the system, this process verifies their log on attempt and creates access tokens based on the user's permission levels.
The SysInternals Tools suite is a set of portable Windows applications that can be used to administer Windows systems (for the most part without requiring installation).
\live.sysinternals.com\tools\procdump.exe -accepteula
Some tools in this suite:
- Process Explorer, an enhanced version of Task Manager
- Process Monitor, used to monitor file system, registry, and network activity related to any process running on the system.
- TCPView, used to monitor internet activity
- PSExec, used to manage/connect to systems via the SMB protocol remotely.
The first step in realizing the importance of service permissions is simply understanding that they exist and being mindful of them. On server operating systems, critical network services like DHCP and Active Directory Domain Services commonly get installed using the account assigned to the admin performing the install. Part of the installation process includes assigning a specific service to run using the credentials and privileges of a designated user, which by default is set within the currently logged-on user context.
It is highly recommended to create an individual user account to run critical network services, called Service Accounts.
Notable built-in service accounts in Windows:
- LocalService
- NetworkService
- LocalSystem
We can also create new accounts and use them for the sole purpose of running a service.
An interactive, or local logon session, is initiated by a user authenticating to a local or domain system by entering their credentials. An interactive logon can be initiated by logging directly into the system, by requesting a secondary logon session using the runas command via the command line, or through a Remote Desktop connection.
Three types:
-
Local System Account:
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
more powerful than accounts in the local administrators group. -
Local Service Account:
NT AUTHORITY\LocalService
granted limited functionality and can start some services -
Network Service Account:
NT AUTHORITY\NetworkService
can establish authenticated sessions for certain network services
They are used by the Windows operating system to automatically start services and applications without requiring user interaction.
- GUI
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- Windows Command Line
- The Command Prompt (CMD)
- Powershell
- Cmdlets
- Aliases
- Scripts
The PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) allows users to write PowerShell scripts on the fly. It also has an autocomplete/lookup function for PowerShell commands. The PowerShell ISE allows us to write and run scripts in the same console, which allows for quick debugging.
We can run PowerShell scripts in a variety of ways. If we know the functions, we can run the script either locally or after loading into memory with a download cradle.
One common way to work with a script in PowerShell is to import it so that all functions are then available within our current PowerShell console session: Import-Module .\PowerView.ps1. We can then either start a command and cycle through the options or type Get-Module to list all loaded modules and their associated commands.
Sometimes we will find that we are unable to run scripts on a system. This is due to a security feature called the execution policy, which attempts to prevent the execution of malicious scripts.
- AllSigned
- Bypass
- Default
- RemoteSigned
- Restricted
- Undefined
- Unrestricted
WMI is a subsystem of PowerShell that provides system administrators with powerful tools for system monitoring. The goal of WMI is to consolidate device and application management across corporate networks.
WMI can be run via the Windows command prompt by typing WMIC to open an interactive shell or by running a command
directly such as wmic computer system get name to get the hostname. We can view a listing of WMIC commands and
aliases by typing WMIC /?.
The WMIC tool is deprecated in Windows 10, version 21H1 and the 21H1 General Availability Channel release of Windows Server. This tool is superseded by Windows PowerShell for WMI. Note: This deprecation only applies to the command-line management tool. WMI itself isn't affected.
WMI can be used with PowerShell by using the Get-WmiObject module instead.
Win + R
Open: mmc
File > Add or remove snap-ins
Allows Linux binaries to be run natively on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
WSL can be installed by running the PowerShell command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
as an Administrator.
Once this feature is enabled, we can either download a Linux distro from the Microsoft Store and install it or manually download the Linux distro of our choice and unpack and install it from the command line.
wsl --install
wsl --list
wsl --set-default-version 2
wsl --install -d distributionName
wsl --setdefault distributionName
wsl npm init
We might need to change a setting and reboot if we use either WSL or VirtualBox:
WSL:
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype auto
VirtualBox (depending on the settings/version):
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype off
We can now enter a bash shell, using bash or wsl command.
We can access the C$ volume and other volumes on the host operating system via the mnt directory, making the transition from the WSL host and the Windows host OS seamless.
- Lower management requirements
- Smaller attack surface
- Less disk space required
- Less memory required
All configuration and maintenance happens through command-line, PowerShell or remote management (MMS/RSAT).
Some GUI is still supported for:
- Registry Editor
- Notepad
- System Information
- Windows Installer
- Task Manager
- PowerShell
Once installed, the initial setup for Server Core can be done via Sconfig, which is a text-based interface (actually a VBScript executed by WScript). Sconfig is used for performing a variety of common commands such as configuring networking, checking for/installing Windows updates, account management, configuring remote management, activating Windows, and more.
Windows follows certain security principles. These are units in the system that can be authorized or authenticated for a particular action. These units include users, computers on the network, threads, or processes.
Each of the security principals on the system has a unique security identifier (SID).
whoami /user
Result:
pcName\userName S-1-5-21-674899381-4069889467-2080702030-1002
- S : SID - Identifies the string as a SID.
- 1 : Revision Level - To date, this has never changed and has always been 1.
- 5 : Identifier-authority - A 48-bit string that identifies the authority (computer/network) that created the SID.
- 21 : Subauthority1 - This is a variable number that identifies the user's relation or group described by the SID to the authority that created it. It tells us in what order this authority created the user's account.
- 674899381-4069889467-2080702030 : Subauthority2 - Tells us which computer (or domain) created the number
- 1002 : Subauthority3 - The RID that distinguishes one account from another. Tells us whether this user is a normal user, a guest, an administrator, or part of some other group
SAM grants rights to a network to execute specific processes.
The access rights themselves are managed by Access Control Entries (ACE) in Access Control Lists (ACL). The ACLs contain ACEs that define which users, groups, or processes have access to a file or to execute a process, for example.
2 types ACL:
- Discretionary Access Control List (DACL)
- System Access Control List (SACL)
Every thread and process started or initiated by a user goes through an authorization process. An integral part of this process is access tokens, validated by the Local Security Authority (LSA). In addition to the SID, these access tokens contain other security-relevant information.
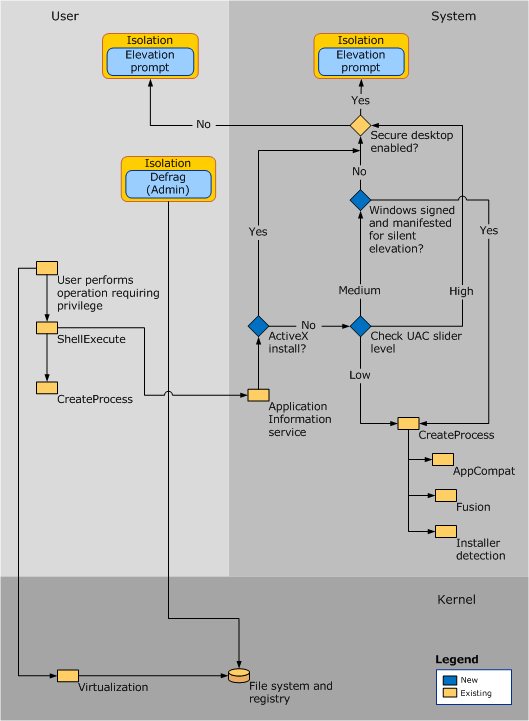
Prevents malware from running or manipulating processes that could damage the computer or its contents through a consent prompt.
The Registry is a hierarchical database, that stores low-level settings for the Windows OS and applications that choose to use it. It is divided into computer-specific and user-specific data.
Win + R
Open: regedit
The entire system registry is stored in several files on the operating system:
C:\Windows\System32\Config\
C:\Windows\Users\<USERNAME>\Ntuser.dat
Contain a logical group of keys, subkeys, and values to support software and files loaded into memory when the operating system is started or a user logs in. These hives are useful for maintaining access to the system.
reg query HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
A whitelist lists approved software applications or executables allowed to be present and run on a system.
A blacklist specifies a list of harmful or disallowed software/applications to block, and all others are allowed to run/be installed.
Whitelisting is recommended by organizations such as NIST, especially in high-security environments.
AppLocker is Microsoft's application whitelisting solution and was first introduced in Windows 7. AppLocker gives system administrators control over which applications and files users can run. It gives granular control over executables, scripts, Windows installer files, DLLs, packaged apps, and packed app installers.
Group Policy allows administrators to set, configure, and adjust a variety of settings. In a domain environment, group policies are pushed down from a Domain Controller onto all domain-joined machines that Group Policy objects (GPOs) are linked to. These settings can also be defined on individual machines using Local Group Policy.
Win + R
Open: gpedit.msc
We can use the PowerShell cmdlet Get-MpComputerStatus to check which protection settings are enabled.
Get-MpComputerStatus | findstr "True"
Windows Defender does very well in monthly detection rate tests compared to other solutions, even paid ones.
Windows Defender will pick up payloads from common open-source frameworks such as Metasploit or unaltered versions of tools such as Mimikatz.
Though it is becoming increasingly difficult, it is still possible to fully bypass Windows Defender protections enforced by the latest version with the most up-to-date definitions installed.
Since we will be using this platform as a penetration testing host, we may run into some issues with Windows Defender finding our tools unsavory. Windows Defender will scan and quarantine or remove anything it deems potentially harmful. To make sure Defender does not mess up our plans, we will add some exclusion rules to ensure our tools stay in place.
Some examples:
Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Users\your user here\AppData\Local\Temp\chocolatey"
Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Users\your user here\Documents\git-repos\
Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Users\your user here\Documents\scripts\
Chocolatey is software management automation for Windows that wraps installers, executables, zips, and scripts into compiled packages.